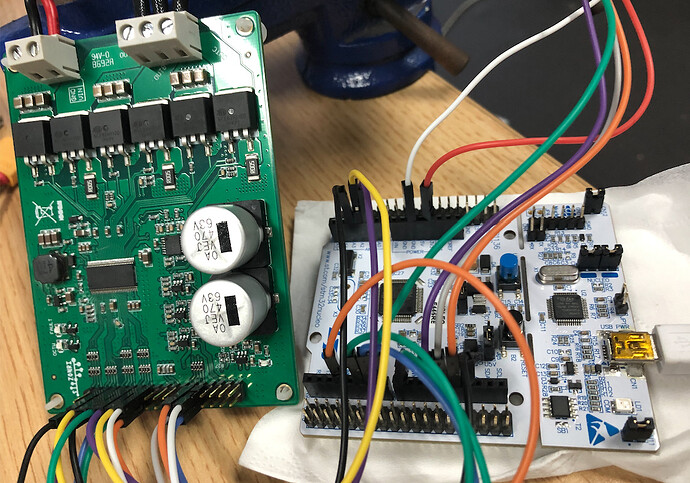
Hi,@Antun_Skuric.
Nice to see you again ,And thank guys for your reply
I’m sorry I didn’t post these days. ![]()
And I’m busy with my work recently. I’ll record a detailed video in a few days to describe the problem. ![]()
Hi,guys.
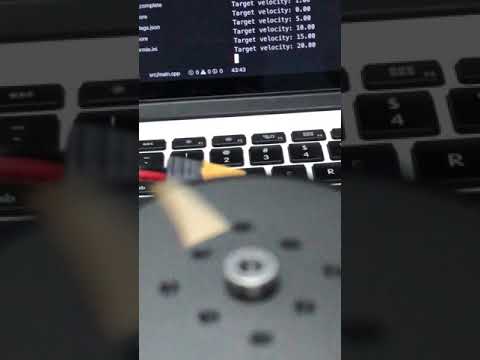
I recorded the serial monitor and the motor together today,If there are any problems, I will continue to improve, thanks everyone.
This is my code.
#include "SimpleFOC.h"
#define EN_GATE 8
#define M_PWM A1
#define M_OC A2
#define OC_ADJ A3
// The cs is Pin7,board is simplebgc mos v1.3
MagneticSensorSPI sensor = MagneticSensorSPI(7, 14, 0x3FFF);
// magnetic sensor instance
// MagneticSensorSPI sensor = MagneticSensorSPI(10, 14, 0x3FFF);
// magnetic sensor instance
//MagneticSensorI2C sensor = MagneticSensorI2C(0x36, 12, 0x0E, 4);
// Motor instance
// BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(9, 5, 6, 7, 8);
// Motor instace(Simplebgc v1.3) (MOT1 9,10,11;MOT2 3,5,6)
BLDCMotor motor = BLDCMotor(3, 5, 6, 14, 8);
void setup() {
// initialise magnetic sensor hardware
sensor.init();
// link the motor to the sensor
motor.linkSensor(&sensor);
// DRV8302 specific code
// M_OC - enable overcurrent protection
pinMode(M_OC,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(M_OC,LOW);
// M_PWM - enable 3pwm mode
pinMode(M_PWM,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(M_PWM,HIGH);
// OD_ADJ - set the maximum overcurrent limit possible
// Better option would be to use voltage divisor to set exact value
pinMode(OC_ADJ,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(OC_ADJ,HIGH);
//
//12V
motor.voltage_power_supply = 12;
// set motion control loop to be used
motor.controller = ControlType::velocity;
motor.PI_velocity.P = 0.001;
motor.PI_velocity.I = 0.2;
//
motor.PI_velocity.voltage_limit = 3;
motor.PI_velocity.voltage_ramp = 1000;
motor.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01;
// use monitoring with serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// comment out if not needed
motor.useMonitoring(Serial);
//
motor.voltage_sensor_align = 0.1;
// initialize motor
motor.init();
// align sensor and start FOC
motor.initFOC();
Serial.println("Motor ready.");
Serial.println("Set the target velocity using serial terminal:");
_delay(1000);
}
// velocity set point variable
float target_velocity = 0;
// utility function enabling serial communication with the user to set the target values
// this function can be implemented in serialEvent function as well
void serialReceiveUserCommand() {
// a string to hold incoming data
static String received_chars;
while (Serial.available()) {
// get the new byte:
char inChar = (char)Serial.read();
// add it to the string buffer:
received_chars += inChar;
// end of user input
if (inChar == '\n') {
// change the motor target
target_velocity = received_chars.toFloat();
Serial.print("Target velocity: ");
Serial.println(target_velocity);
// reset the command buffer
received_chars = "";
}
}
}
void loop() {
//unsigned int timecnt;
// main FOC algorithm function
// the faster you run this function the better
// Arduino UNO loop ~1kHz
// Bluepill loop ~10kHz
//timecnt = millis()-timecnt;//Read once before testing the function,The unit is us
motor.loopFOC();
// Motion control function
// velocity, position or voltage (defined in motor.controller)
// this function can be run at much lower frequency than loopFOC() function
// You can also use motor.move() and set the motor.target in the code
motor.move(target_velocity);
// function intended to be used with serial plotter to monitor motor variables
// significantly slowing the execution down!!!!
// motor.monitor();
// user communication
serialReceiveUserCommand();
// timecnt = millis()-timecnt;//Subtract the last result after the function test is completed
// Serial.print("timecnt=");//print the "timecnt"
// Serial.println(timecnt );
}
Your P is quite low. Are you tuning at low speed? I find it hard to tune P at low speed, instead i tune at half max speed (say 20 radians/s) and tune P first (holding i to zero). If P can give you 70% of target speed (i.e 14 rad/s) without oscillation, then later add I.
What was the clock speed of your mcu?