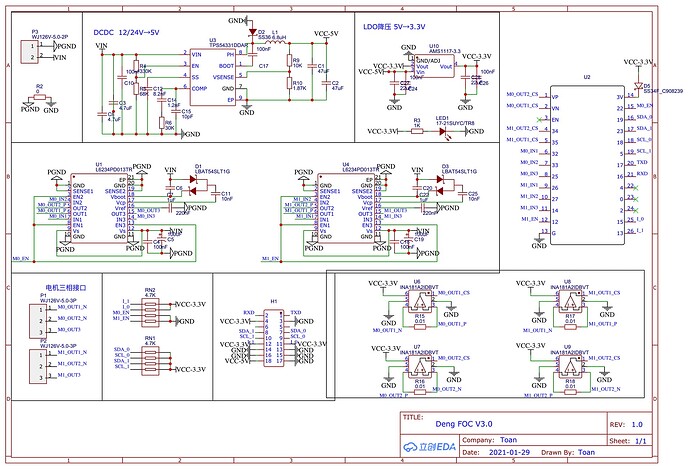
issues reading the total current sent to the motor. My set up consists of a GM3506 Gimbal Motor (5.6ohms) a MKS Dual FOC board and an esp32 dev board. According to the schematics the MKS board has a 0.01ohm resistor and a op amp gain of 50. I set that up using InlineCurrentSense(0.01f, 50.0f, 35, 34); but when I call getDCCurrent() it is inaccurate. From following tests I noted that the power supply current was 0.27amps while the getDCCurrent() read about 1.2 amps. I also tried at a current of 1.10 amps from the power supply and the getDCCurrent() read about 2.4 amps. So it’s consistently reading higher than the real current. I cant figure out what is going on. Ive tried messing with th eInlineCurr entSense(0.01f, 50.0f, 35, 34); values just in case and also changing the the gain_b and gain_a to -1. I also switched out the esp32 incase its ADC was the problem but to no avail. Please I would appreciate any help with this.
Notes: using Simple FOC library 2.3.2
code for reference:
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <SimpleFOC.h>
MagneticSensorSPI sensor2 = MagneticSensorSPI(AS5147_SPI, 15);
BLDCMotor motor2 = BLDCMotor(11);
BLDCDriver3PWM driver2 = BLDCDriver3PWM(26, 27, 14, 12); //MKS esp32
InlineCurrentSense current_sense2 = InlineCurrentSense(0.01f, 50.0f, 35, 34); //MKS dual foc esp32
// Motor and Actuator 2 parameters
float target_angle_m2 = 0; // Radians - motor
float target_angle_a2 = 0; // Radians - actuator
float angle_a2; // Radians
float velocity_a2; // Radians per second
float angle_offset_m2 = 0; // Radians
float joint_stop_a2 = 15 * (PI / 180.0); // Radians - Joint stop angle from zero
unsigned long homingTime;
// instantiate the commander
Commander command = Commander(Serial);
void doTarget(char* cmd) {
command.scalar(&target_angle_a2, cmd);
}
void Homing() {
bool homing_m2 = true; //when homing true, false when home has been found
homingTime = millis();
target_angle_m2 = motor2.shaft_angle;
motor2.move(target_angle_m2);
while (homing_m2) {
motor2.loopFOC();
motor2.move(target_angle_m2);
if (millis() - homingTime > 50) {
//Motor 2 Homing
if (abs(motor2.voltage.q) < 1.5 && homing_m2) {
target_angle_m2 -= .3;
motor2.move(target_angle_m2);
} else if (homing_m2) {
angle_offset_m2 = motor2.shaft_angle;
homing_m2 = false;
target_angle_m2 = .5 + angle_offset_m2;
motor2.loopFOC();
Serial.print("Homing Found M2");
Serial.print(angle_offset_m2);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.print(" M2 Tθ:");
Serial.print(target_angle_m2);
Serial.print(" V:");
Serial.println(motor2.voltage.q);
//Serial.print(" A:");
//Serial.println(current_sense1.getDCCurrent()); // total current in Amps
homingTime = millis();
}
}
}
void setup() {
// use monitoring with serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// enable more verbose output for debugging
// comment out if not needed
SimpleFOCDebug::enable(&Serial);
// initialise magnetic sensor hardware
sensor2.init();
// link the motor to the sensor
motor2.linkSensor(&sensor2);
driver2.pwm_frequency = 20000;
// driver config
// power supply voltage [V]
driver2.voltage_power_supply = 24;
driver2.voltage_limit = 24; // max voltage to motor
driver2.init();
// link the motor and the driver
motor2.linkDriver(&driver2);
// link current sense and the driver
current_sense2.linkDriver(&driver2);
// current sense init hardware
current_sense2.init();
//current_sense2.gain_b *= -1;
//current_sense2.gain_a *= -1;
// link the current sense to the motor
motor2.linkCurrentSense(¤t_sense2);
// choose FOC modulation (optional)
motor2.foc_modulation = FOCModulationType::SpaceVectorPWM;
//motor.torque_controller = TorqueControlType::foc_current;
//motor.current_limit = 1; // Amp limit
// set motion control loop to be used
motor2.controller = MotionControlType::angle;
// contoller configuration
// default parameters in defaults.h
// velocity PI controller parameters
motor2.PID_velocity.P = .1;
motor2.PID_velocity.I = 2;
motor2.PID_velocity.D = 0;
// maximal voltage to be set to the motor
motor2.voltage_limit = 12; //8
// velocity low pass filtering time constant
motor2.LPF_velocity.Tf = 0.01f;
// angle P controller
motor2.P_angle.P = 10;
// maximal velocity of the position control
motor2.velocity_limit = 190;
// comment out if not needed
motor2.useMonitoring(Serial);
// initialize motor
motor2.init();
// align sensor and start FOC;
motor2.initFOC();
// add target command T
command.add('T', doTarget, "target angle");
Serial.println(F("Motor ready."));
Serial.println(F("Set the target angle using serial terminal:"));
_delay(1000);
// Homing %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
Homing();
target_angle_a2 = 0;
}
void loop() {
//PhaseCurrent_s currents = current_sense.getPhaseCurrents();
// main FOC algorithm function
// the faster you run this function the better
motor2.loopFOC();
target_angle_m2 = target_angle_a2 * 9;
motor2.move(target_angle_m2 + angle_offset_m2 + (joint_stop_a2 * 9));
// monitor angles & velocity at ~10 Hz
static unsigned long t_last = 0;
if (millis() - t_last > 150) {
t_last = millis();
angle_a2 = (motor2.shaft_angle - angle_offset_m2) / 9 - joint_stop_a2;
velocity_a2 = motor2.shaft_velocity / 9;
// Actuator Stats:
Serial.print(" θ2:");
Serial.print(angle_a2, 3);
Serial.print(" ω2:");
Serial.print(velocity_a2, 3);
Serial.print(" Vq2:");
Serial.print(motor2.voltage.q, 2);
Serial.print(" A2:");
Serial.print(current_sense2.getDCCurrent()); // total current in Amps
Serial.println();
// user communication
command.run();
}
}